If you have trouble losing weight despite your best efforts, this is because obesity is a complex disease with many causes. A family history of weight issues can make it more likely that you’ll have the same issues managing your weight. A diet high in ultra-processed foods, sugar, and fat and being sedentary also contribute to weight gain. Stress and struggles with mental health, including medications to treat certain mental health conditions, poor sleep, and hormonal changes, are all factors that further contribute to weight gain.
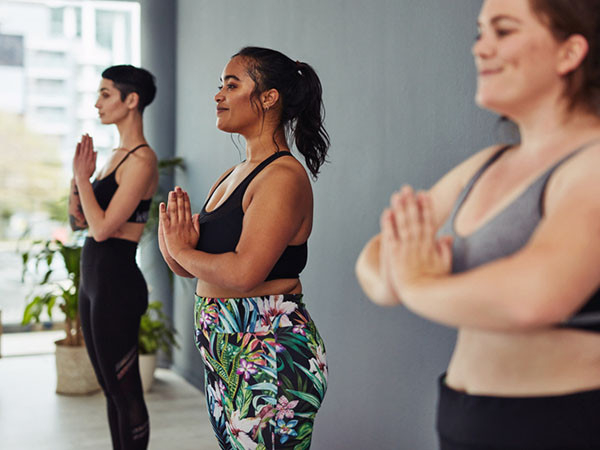
There are many ways to combat excess weight, but there is no single solution. If you are trying to lose or maintain your weight, you may want to try yoga. There is good research that yoga may help you manage stress, improve your mood, curb emotional eating, and create a community of support, all of which can help with weight loss and maintenance.
Yoga can also help you burn calories, as well as increase your muscle mass and tone. Yoga may reduce joint pain, which in turn allows you to exercise more and increase your daily activities. These are only some of the many benefits of yoga.
Yoga can help you manage stress that can impact weight gain
Yoga is derived from the Sanskrit word yuj, which means to unite the body, mind, and emotions. It is a holistic mind-body practice that improves many of the causes of weight gain.
Some people may experience stress as physical pain or sleep deprivation, or it may be psychological and cause feelings of anxiety and agitation. Stress leads to an increase in the hormone cortisol. Cortisol increases abdominal fat, decreases muscle mass, causes cravings for fat and sugar-rich food, and thus can lead to obesity.
Yoga can decrease stress and cortisol levels, enhance mood, decrease anxiety and depression, improve sleep, and improve chronic conditions such as hypertension and diabetes, reducing the need for medications that can cause weight gain.
Yoga is not a band-aid for excess weight, but it may work on the underlying causes. Its benefits extend beyond the calories-in-versus-calories-out equation.
Yoga can improve mindfulness related to eating behaviors
Most of us who crave ice cream after 9 pm or can’t stop eating potato chips know that these behaviors hurt our chances of losing weight. We all know that eating vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, etc. is good for our health and weight. While this knowledge is necessary, it seems insufficient to help us stick to our healthy eating plans.
One of yoga’s benefits is that it improves mindfulness of the body and awareness of body sensations. This is why yoga is called “moving meditation.” Research shows that you don’t have to do any formal sitting meditation to get the mindfulness benefits of yoga.
By improving mindfulness, yoga decreases emotional eating, stress eating, and binge eating. These habits sabotage our weight loss efforts and can cause a negative spiral of guilt and shame, which often leads to giving up.
A study published in 2015 showed that practicing yoga led to healthier eating, including lower fat intake and an increase in vegetables and whole grains.
The bottom line: the best diet plan is the one that you can stick with over the long term, and by improving mindfulness, yoga can help you make healthier food choices.
A yoga community can provide acceptance and support
Going to a gym can be intimidating, and may provoke feelings of not belonging for some people with larger bodies. By contrast, yoga culture embodies kindness, support, and self-acceptance.
Yoga teachers and advanced practitioners can serve as role models and inspire newer students to live a healthier lifestyle. Research shows that social networks influence behaviors that affect weight. The yoga network encourages positive health behaviors, and being a part of such a community can make a meaningful difference for weight loss. This type of community can be hard to find with other types of exercise.
Practitioners should look for a safe, comfortable environment. A welcoming yoga group may help you improve your self-esteem and confidence. Find a local studio that feels nurturing and not overwhelming, with other practitioners at your level. Teachers can help beginners or those with physical limitations by modifying poses. You might have to try a few different classes before you find an instructor or a class that you like. Don’t give up after the first one!
If you can’t find a local studio, there are always online options on YouTube and Instagram, with classes at all levels. There are instructors who understand what it is like to be a larger size, and having an inclusive, body-affirming attitude shows that yoga is not just for “skinny people.” Some share inspirational stories of how yoga helped them overcome their own weight struggles, depression, and binge eating. If you are a beginner, consider signing up for a short challenge to get committed to the practice.
The benefits of yoga are universal — no matter what your shape or size. It can take weeks or months to establish a yoga practice, and frequent practice is key for long-lasting benefits.
Follow Dr. Anekwe on Twitter @Chikagirl
Follow Dr. Reddy on Twitter @NiyotiReddy